Orchestration vs Job Scheduling: Understanding the Differences and Applications in AI and HPC
In modern computing environments, managing workloads efficiently is critical. Two key concepts that often come up in this context are orchestration and job scheduling. While they may seem similar, they serve distinct purposes and are designed for different types of workloads and environments. This article explores the differences between orchestration and job scheduling, their features, and their relevance to AI (Artificial Intelligence) and HPC (High-Performance Computing).
Table Of Content
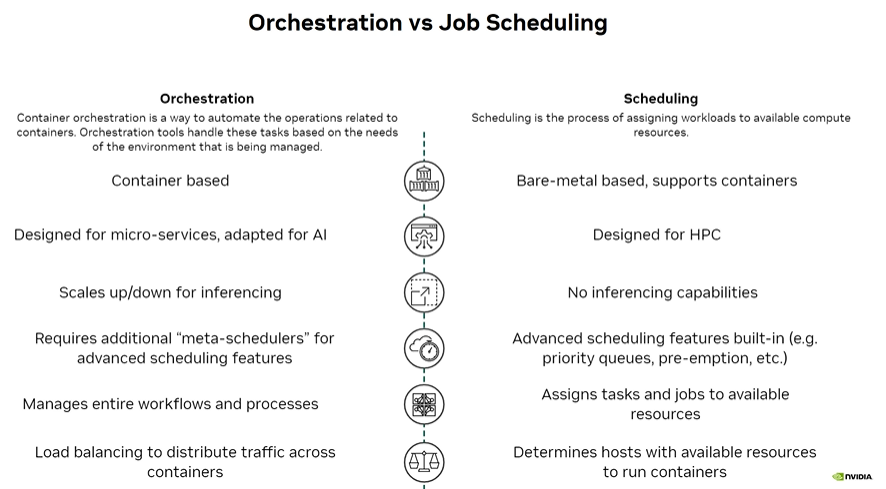
What is Orchestration?
Orchestration refers to the automation of operations related to containers. Containers are lightweight, portable units that package software and its dependencies, enabling consistent deployment across different environments. Orchestration tools automate the deployment, scaling, and management of these containers based on the needs of the environment.
Key Characteristics of Orchestration:
- Container Based: Orchestration is inherently designed around containerized applications, making it ideal for microservices architectures.
- Designed for Microservices and AI: It is well-suited for AI workloads that rely on microservices and require dynamic scaling.
- Scales Up/Down for Inferencing: Orchestration platforms like kubernetes can automatically scale resources up or down to handle AI inferencing demands efficiently.
- Requires Additional “Meta-Schedulers”: For advanced scheduling features, orchestration often relies on additional meta-schedulers.
- Manages Entire Workflows and Processes: Beyond just scheduling tasks, orchestration manages complex workflows and interdependent processes.
- Load Balancing: It distributes traffic evenly across containers to optimize resource utilization and performance.
What is Job Scheduling?
Job scheduling is the process of assigning workloads or jobs to available compute resources. It is traditionally used in HPC environments where large-scale computational tasks need to be efficiently allocated to physical or virtual machines.
Key Characteristics of Job Scheduling:
- Bare-Metal Based, Supports Containers: Scheduling primarily operates on bare-metal servers but can also support containerized workloads.
- Designed for HPC: It is optimized for high-performance computing tasks that require significant computational power.
- No Inferencing Capabilities: Unlike orchestration, job scheduling does not inherently support AI inferencing.
- Advanced Scheduling Features Built-In: Features such as priority queues, pre-emption, and resource reservations are integral to job schedulers.
- Assigns Tasks and Jobs to Available Resources: The scheduler ensures that jobs are allocated to the most appropriate resources based on availability and priority.
Comparing Orchestration and Job Scheduling
| Feature | Orchestration | Job Scheduling |
|---|---|---|
| Basis | Container based | Bare-metal based, supports containers |
| Design Focus | Microservices, adapted for AI | High-Performance Computing (HPC) |
| Scaling | Scales up/down for AI inferencing | No inferencing capabilities |
| Scheduling Features | Requires additional meta-schedulers for advanced features | Advanced scheduling features built-in (priority queues, pre-emption) |
| Workflow Management | Manages entire workflows and processes | Assigns tasks and jobs to available resources |
| Load Balancing | Distributes traffic across containers | Not typically focused on load balancing |
Applications in AI and HPC
In AI Environments:
Orchestration is the preferred approach for managing AI workloads, especially those built on microservices and containerized applications. It allows dynamic scaling to meet the fluctuating demands of AI inferencing and training. Orchestration platforms like Kubernetes provide the flexibility to automate complex workflows and ensure efficient resource utilization.
In HPC Environments:
Job scheduling remains the backbone of HPC systems, where large computational jobs need to be queued and executed on powerful bare-metal servers. HPC schedulers like Slurm or PBS manage job priorities, resource allocation, and execution order to maximize throughput and minimize wait times.
Conclusion
While orchestration and job scheduling both aim to optimize workload management, they cater to different environments and requirements. Orchestration excels in containerized, microservices-based AI applications with dynamic scaling and workflow management. Job scheduling is tailored for HPC workloads requiring robust resource allocation and advanced scheduling features.
Understanding these differences helps organizations choose the right tools and strategies to efficiently manage their AI and HPC workloads, ensuring optimal performance and resource utilization.
Image Source: NVIDIA