NVIDIA Networking in AI
Have you ever wondered what kind of networking topology powers an AI factory?
Table Of Content
Unlike traditional data centers that rely on north-south Ethernet networks, AI training environments require a different approach. The typical Ethernet setup becomes a bottleneck for the demanding generative AI workloads due to its limited speed and higher latency. Instead, AI factories use InfiniBand networking, a high-performance technology designed for low latency, high throughput, and minimal processing overhead.
What is InfiniBand?
InfiniBand is a cutting-edge networking technology widely adopted in high-performance computing and AI. It delivers exceptional data transfer speeds with very low latency, making it ideal for large-scale AI model training. The InfiniBand specification is maintained by the InfiniBand® Trade Association (IBTA), ensuring industry-wide standards and interoperability.
Key Feature: Direct Memory Access (DMA) and RDMA
One of InfiniBand’s standout features is Direct Memory Access (DMA), which allows devices to access host memory directly without involving the CPU. This capability is extended through Remote Direct Memory Access (RDMA), enabling data transfers with minimal CPU intervention.
InfiniBand network adapters, known as Host Channel Adapters (HCAs), incorporate hardware offloading to accelerate data movement, reducing CPU overhead significantly.
Benefits of RDMA include:
- Efficient data transfer by bypassing the OS to enable the fastest possible access to remote data.
- Optimized computing that reduces power consumption, cooling needs, and space requirements.
- Compatibility with message passing, sockets, and storage protocols.
- Support by all major operating systems.
Traditional Data Flow (Before GPU Direct)
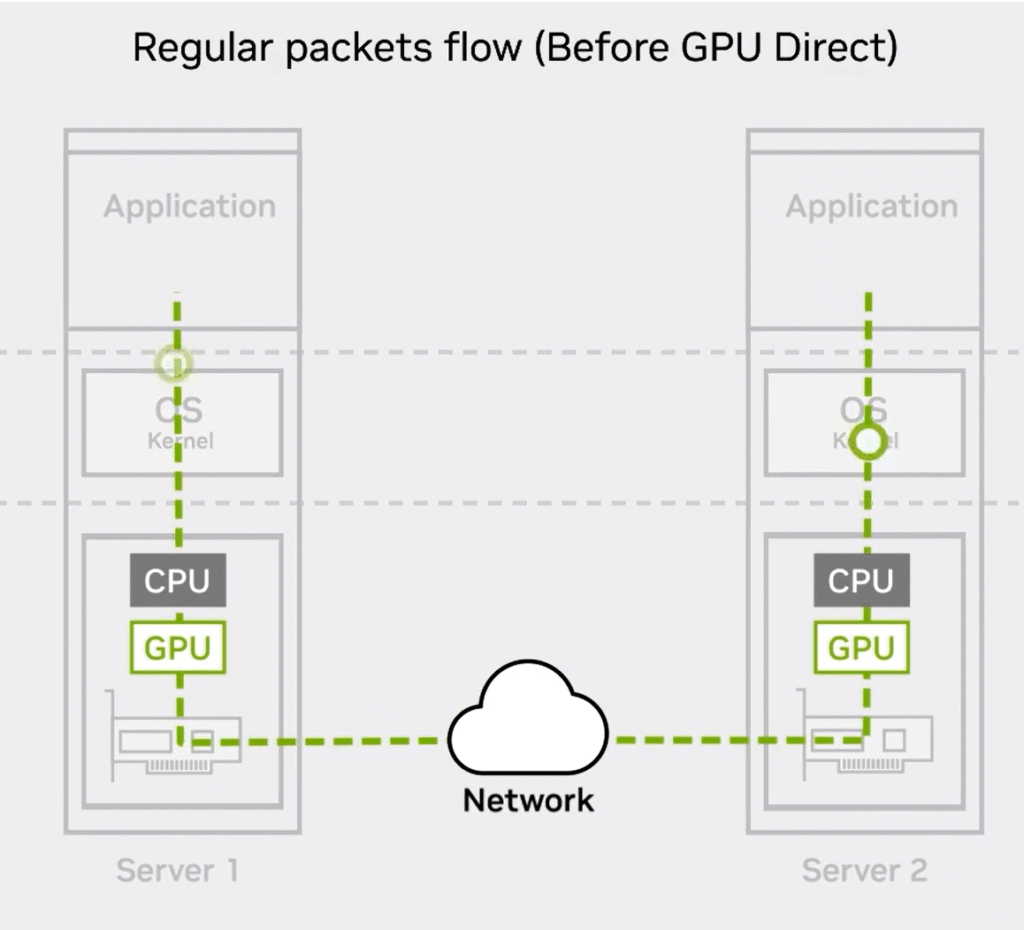
In a typical server-to-server communication without GPU Direct, the data flow involves multiple stages:
Server 1:
- The application generates data to be sent.
- Data passes through the Operating System (OS) kernel.
- The CPU processes the data.
- The CPU transfers data to the GPU.
- The GPU sends data through the network interface to the network.
Server 2:
- The GPU receives incoming data from the network.
- Data is passed from the GPU to the CPU.
- The CPU sends data up to the OS kernel.
- The OS kernel delivers data to the application.
Key points:
- Data transitions multiple times between OS kernel, CPU, and GPU on both servers.
- OS kernel involvement adds processing overhead.
- CPU involvement causes latency and extra data copying between CPU and GPU memory.
Optimized Data Flow with GPU Direct
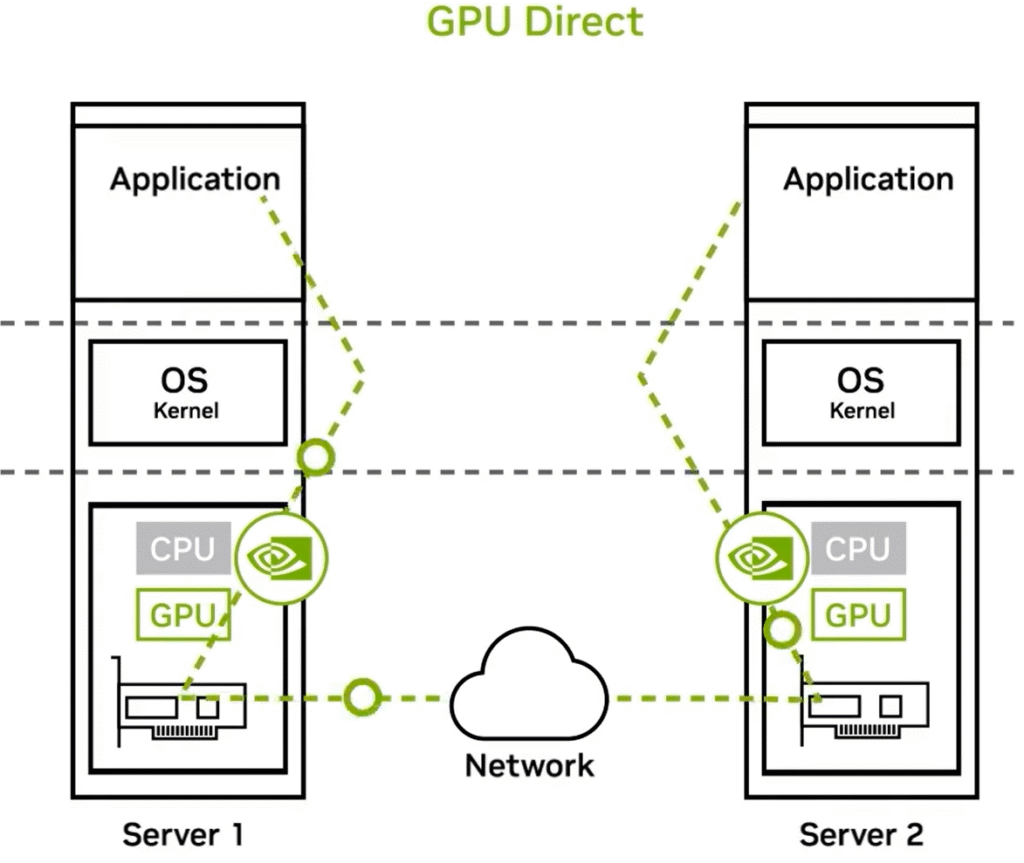
GPU Direct technology revolutionizes this process by enabling direct data transfers between GPUs over the network, bypassing the CPU and OS kernel for most of the data path.
How it works:
- The application on Server 1 initiates data transfer directly through the GPU.
- The GPU communicates straight with the network interface card (NIC) to send data.
- Data travels across the network to Server 2’s NIC.
- The NIC transfers data directly to Server 2’s GPU.
- The GPU makes data available to the application, bypassing CPU and OS kernel involvement.
Benefits of GPU Direct:
Reduced latency and CPU overhead by avoiding CPU and OS kernel processing.
Direct GPU-to-GPU communication enhances throughput and efficiency.
Minimized data copying eliminates unnecessary memory transfers between CPU and GPU.
InfiniBand networking combined with GPU Direct technology forms the backbone of modern AI infrastructure. This setup delivers the high throughput, low latency, and efficient data movement essential for training large-scale AI models. By minimizing CPU involvement and enabling direct GPU communication over the network, NVIDIA’s networking solutions significantly boost performance and resource efficiency in AI factories.